The NEB PCR Cloning Kit contains an optimized 2X Cloning Master Mix with a proprietary ligation enhancer and a linearized vector that uses a novel mechanism for background colony suppression to give a low background.
It allows simple and quick cloning of any PCR amplicon, whether the amplification reactions are performed with proofreading DNA polymerases, such as Q5® or Phusion® which produce blunt ends; or nonproofreading DNA polymerases, such as Taq or Taq mixes (OneTaq®, LongAmp™ Taq) which produce single base overhangs. This is possible due to “invisible” end polishing components in the master mix that are active during the ligation step.
The kit also allows direct cloning from amplification reactions without purification, and works well whether or not the primers used in the PCR possess 5´-phosphate groups.
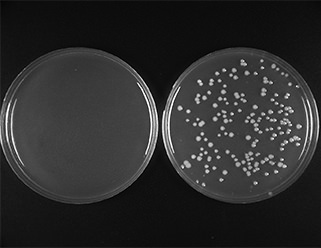
A 500 bp PCR product incubated with the linearized vector in a 3:1 ratio according to recommended protocol. 2 μl of reaction was transformed into provided NEB 10-beta Competent E. coli and 1/20th of the outgrowth was plated. Left plate serves as the control, with vector backbone only, right plate contains PCR insert.
Advantages
- Easy cloning of all PCR products, including blunt and TA ends
- Fast cloning experiments with 5-minute ligation step
- Simplified screening with low/no colony background and no blue/white selection required
- Save time by eliminating purification steps
- Flanking restriction sites available for easy subcloning, including choice of two single digest options
- Provided analysis primers allow for downstream colony PCR screening or sequencing
- Ready-to-use kit components include 1 kb control amplicon, linearized cloning vector and single-use competent E. coli
- Longer shelf life (12 months), as compared to some commercially available products
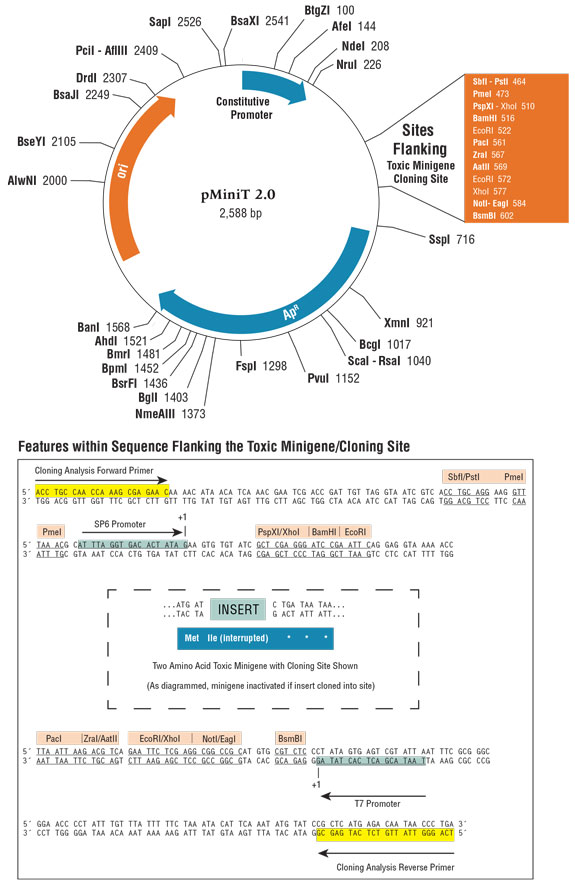
pMiniT Vector Map
Map shown above displays the construct formed if no insert is present. Unique restriction sites are shown in black. Additional restriction sites that can be used for subcloning are shown in red. Expanded box below shows location of sequencing primers, restriction sites for subcloning, and placement of insertion site within the toxic minigene.
Further information can be found in our Technical Resources section or at neb.com


